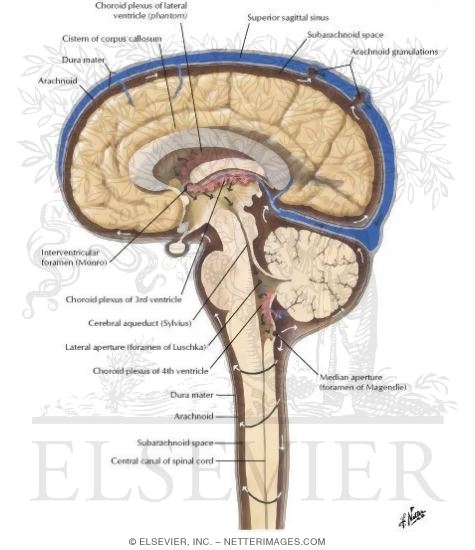
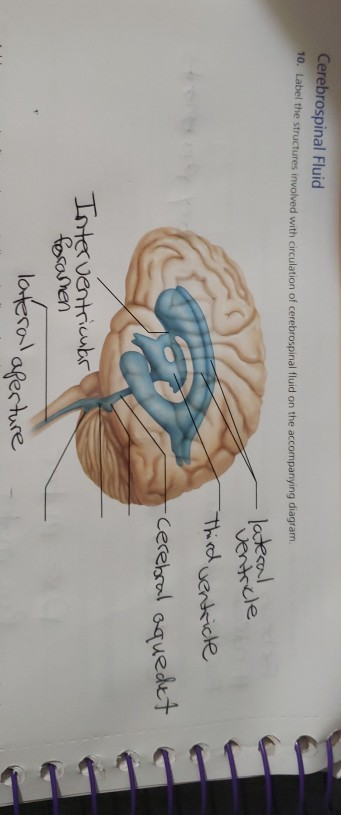
40 structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid
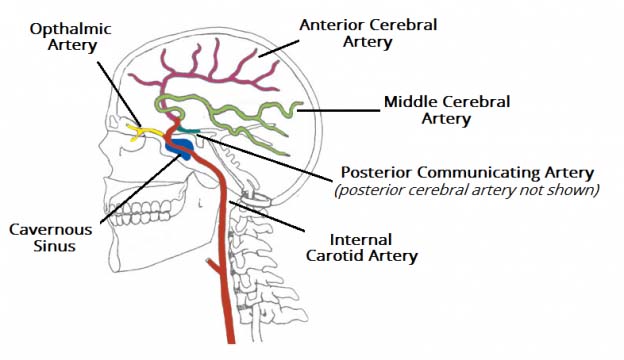
Anatomy and Ultrastructure - The Cerebral Circulation - NCBI Bookshelf Cerebral Vascular Architecture. The pial vessels are intracranial vessels on the surface of the brain within the pia-arachnoid (also known as the leptomeninges) or glia limitans (the outmost layer of the cortex comprised of astrocytic end-feet) [].Pial vessels are surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and give rise to smaller arteries that eventually penetrate into the brain tissue (). Home Page: American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology Apr 02, 2021 · AJOG's Editors have active research programs and, on occasion, publish work in the Journal. Editor/authors are masked to the peer review process and editorial decision-making of their own work and are not able to access this work in the online manuscript submission system.
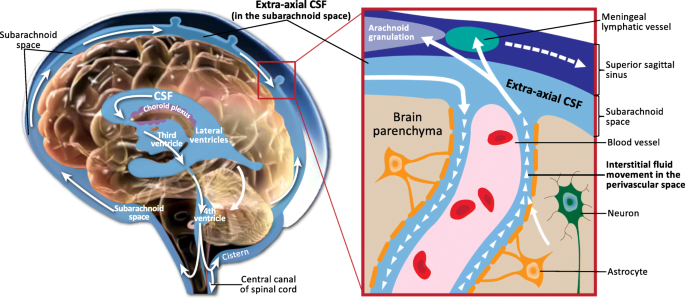
CSF Cerebrospinal Fluid - Physiopedia When the CSF pressure is greater than the venous pressure, CSF will flow into the blood stream. However, the arachnoid villi act as "one way valves"...if the CSF pressure is less than the venous pressure, the arachnoid villi will NOT let blood pass into the ventricular system Image 2 shows Schematic of CSF circulation, CSF outflow systems, and the anatomy of various CSF compartments.

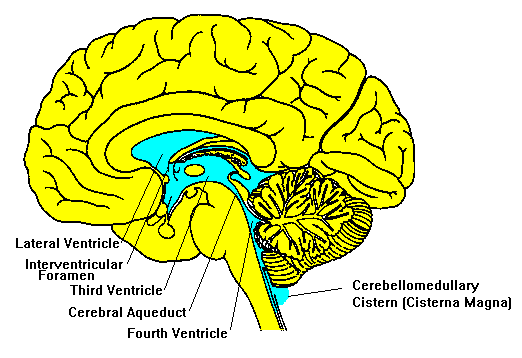
Structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid
The function and structure of the cerebrospinal fluid outflow system The functional anatomy of the structures responsible for the return of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to the general circulation is based on somewhat conflicting evidence as to their location, anatomical features, and functional capabilities. Circulation of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Flashcards | Quizlet Central canal of spinal cord 2. To the subarachnoid space via : two lateral apertures (holes or gaps) & one median aperture 3. Through extensions called arachnoid villi that delivers the CSF back into the superior sagittal sinus Arachnoid villi form large clusters in adults, called arachnoid granulations Circulation of CSF Circulation of CSF 2 Solved > 14.Label the structures involved with circulation of ... 14.Label the structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid on the accompanying diagram. Add arrows to the figure above to indicate the flow of cerebrospinal fluid from its formation in the lateral ventricles to the site of its exit from the fourth ventricle. Then fill in the blanks in the following paragraph. Solution 5 (1 Ratings )
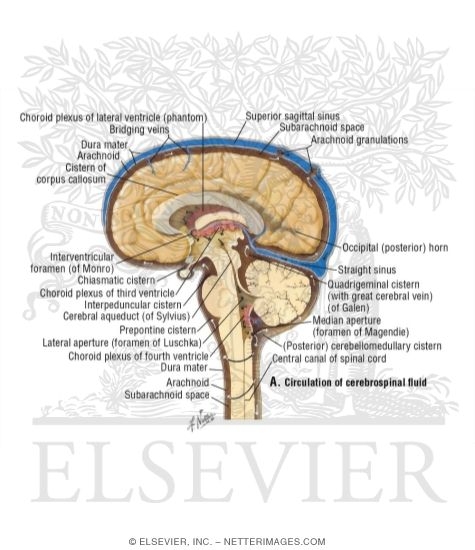
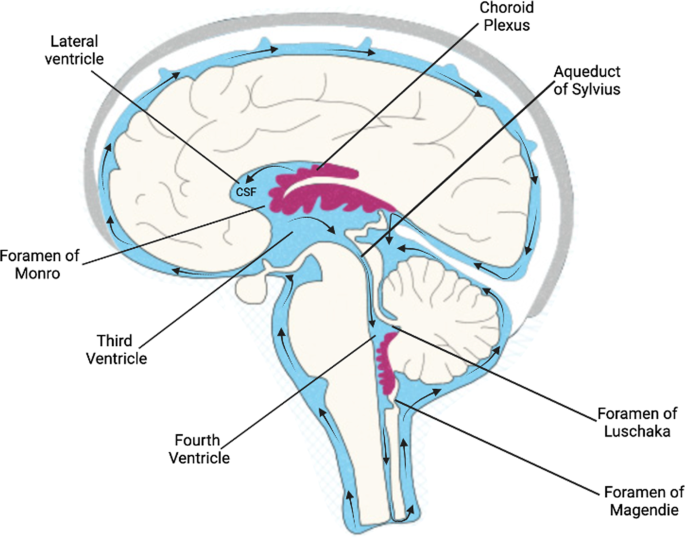
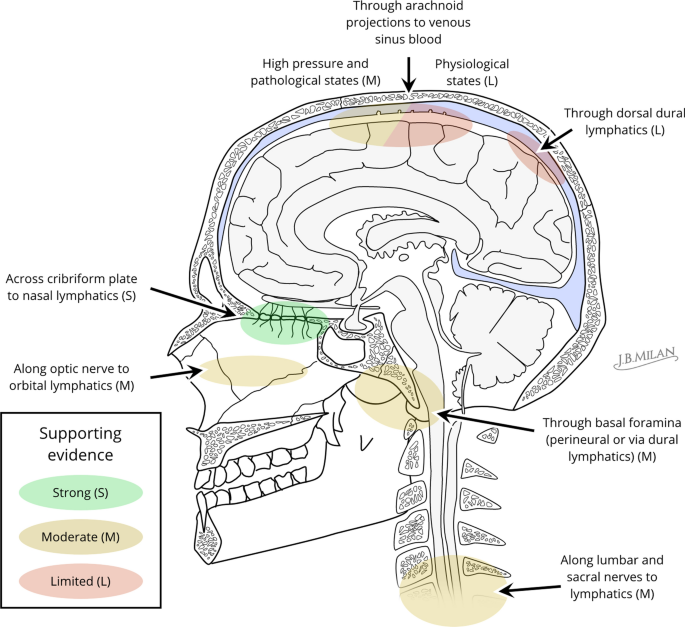
Structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. Home Page: The Annals of Thoracic Surgery Apr 11, 2022 · by Brian Mitzman, MD, FACS, and Jo Chikwe, MD, FRCS. The October edition of Editors’ Choice is coauthored by Senior Editor Brian Mitzman, MD, bringing general thoracic surgery expertise to highlight some of the 50 high-quality original research, reviews, and editorials in this issue of The Annals. Circulation of Cerebrospinal Fluid Flashcards | Quizlet Choroid plexus in the fourth ventricle adds more CSF. 5. CSF flows out Median and Lateral Apertures or through Central Canal of Spinal Cord. 6. CSF fills subarachnoid space and bathes external surfaces of brain and spinal cord. 7. At arachnoid villi, CSF flows to Superior Sagittal Sinus and into Internal Jugular Vein. 8. formation and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid - Quizlet 1) upward from the base of brain and over cerebrum and cerebellum toward longitudinal fissure. 2) into arachnoid villi. 3) into venous sinuses (spaces filled with blood) 4) into veind found in teh meninges adn finally into the internal jugular vein (fluid has now been returned to the circulatory system) what are ventricles. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): Composition, Circulation and Function Most of CSF gets absorbed into arachnoid villi and granulations which dip into subdural venous sinuses. Subarachnoid spaces can be reached either by lumbar or cisternal puncture. Lumbar puncture is preferred because cisternal puncture requires insertion of needle into subarachnoid spaces near brainstem region.
Cerebrospinal fluid circulation: What do we know and how do we know it ... Movement and Absorption of Cerebrospinal Fluid After production, CSF movement generally occurs through the ventricular system, assisted, in part, by ciliated ependyma which beat in synchrony. [ 19] CSF net flow is still generally believed to flow through the ventricular system, initiated at the lateral ventricles. [ 5] Solved Cerebrospinal Fluid 10. Label the structures involved - Chegg Science; Anatomy and Physiology; Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers; Cerebrospinal Fluid 10. Label the structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid on the accompanying diagram lateconl Ventrcle Cerehsol oquedet resosmen afer ture Glossary | Linus Pauling Institute | Oregon State University Cerebrospinal fluid the fluid that bathes the brain and spinal cord. Cerebrovascular disease disease involving the blood vessels supplying the brain, including cerebrovascular accident (CVA), also known as a stroke. Cerebrum the upper part of the brain that is involved in conscious mental functions. Ceruloplasmin Physiology, Cerebral Spinal Fluid - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is an ultrafiltrate of plasma contained within the ventricles of the brain and the subarachnoid spaces of the cranium and spine.[1] It performs vital functions, including providing nourishment, waste removal, and protection to the brain.[2] Adult CSF volume is estimated to be 150 ml, with a distribution of 125 ml within the subarachnoid spaces and 25 ml within the ...
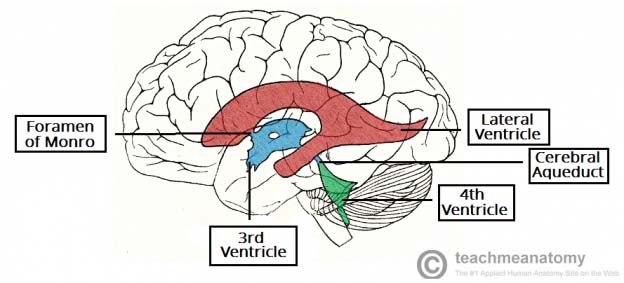
Flow of Cerebrospinal Fluid Flashcards | Quizlet Choroid plexus in the lateral ventricles produces CSF. What happens at stage 1? CSF flows through interventricular foramina into third ventricle. What happens at stage 2? Choroid plexus in the third ventricle adds more CSF. What happens at stage 3? CSF flows down cerebral aqueduct to fourth ventricle. What happens at stage 4? Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Normal CSF flow is a consequence of both transmitted choroidal arterial pulsations and bulk flow resulting from continuous CSF production. Radionuclide CSF FS, or so-called radionuclide ventriculography, provides a safe physiological assessment of the functional anatomy of the various CSF compartments and constitutes the technique of choice to evaluate CSF flow dynamics as mentioned above. 2 ... Solved Label the structures involved with circulation of | Chegg.com Label the structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid on the accompanying diagram. (These structures are identified by leader lines.) Question: Label the structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid on the accompanying diagram. (These structures are identified by leader lines.) Cerebrospinal Fluid - Contents of CSF - Flow of CSF - TeachMePhysiology The CSF is produced by the choroid plexus which covers two lateral ventricles, and the roof of the third and fourth ventricles. Around 500 ml of CSF is produced each day, with around 150 ml being present in the body at any given time. The choroid plexus is composed of fenestrated capillary loops, covered by a layer of specialised ependymal cells.
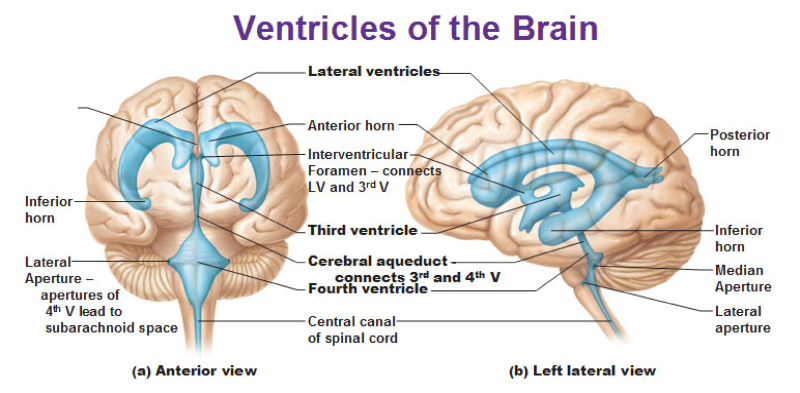
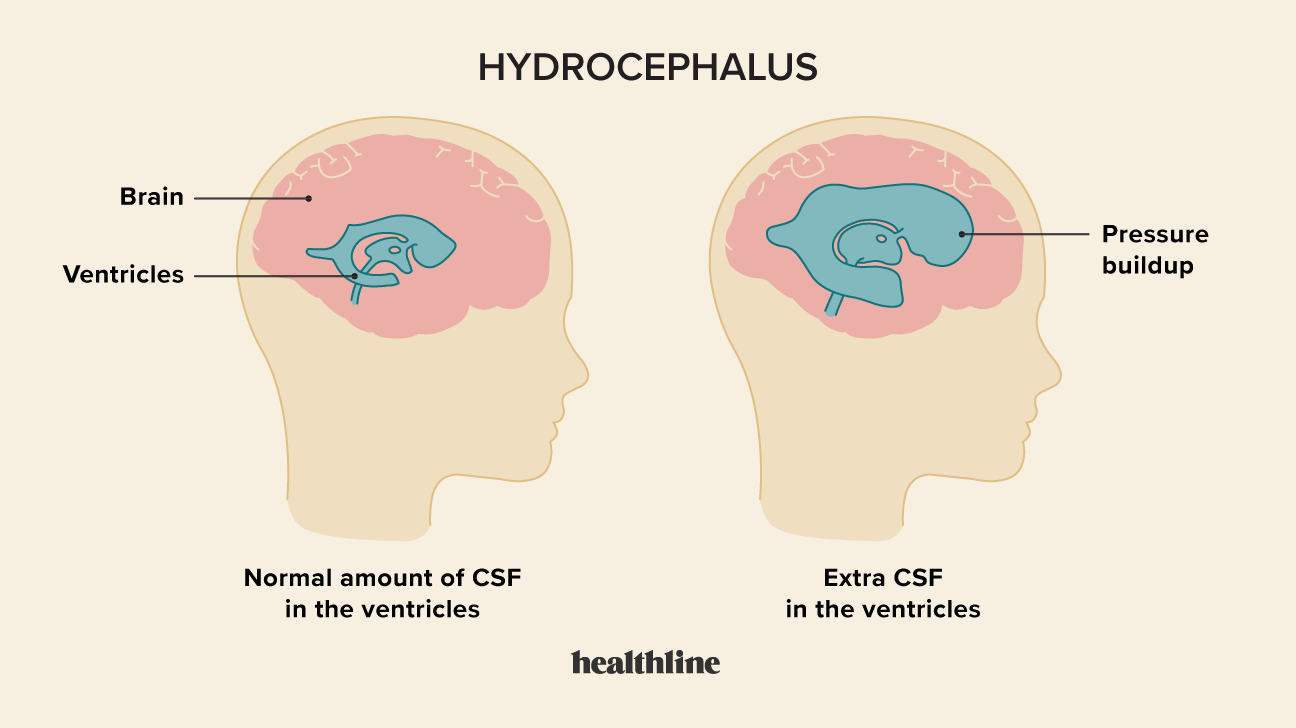
Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics 6.6 Circulation of the Cerebrospinal Fluid CSF flows internally through the ventricles, from lateral ventricles to the third ventricle to the cerebral aqueduct to the fourth ventricle. The CSF passes through several points where blockage or obstruction could precipitate internal hydrocephalus and increased intracranial pressure.
Anatomy, Head and Neck, Cerebrospinal Fluid - NCBI Bookshelf Examples are a ventriculoperitoneal shunt, ventriculoatrial shunt, or ventricular-pleural shunt. The lumbar-peritoneal shunt drains excess CSF from the spinal subarachnoid space into the peritoneum. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy is a recent surgical approach, often done with cauterization of the choroid plexus. Color: clear or colorless
The function and structure of the cerebrospinal fluid outflow system ported this an atomic view o f the CSF syst em with flow in the direction of the sinus beginning at 20 to 50 mm H 2 0 with a cur ve convex to the pressure ax is (Figure 3) .
Inflammation - Wikipedia Inflammation has also been classified as Type 1 and Type 2 based on the type of cytokines and helper T cells (Th1 and Th2) involved. Inflammation is not a synonym for infection. Infection describes the interaction between the action of microbial invasion and the reaction of the body's inflammatory response—the two components are considered ...
Cerebrospinal fluid - Wikipedia Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates. CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations. There is about 125 mL of CSF at any one time, and about ...
Brain - Wikipedia Even though it is protected by the skull and meninges, surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the bloodstream by the blood–brain barrier, the delicate nature of the brain makes it vulnerable to numerous diseases and several types of damage. In humans, the effects of strokes and other types of brain damage have been a key source ...
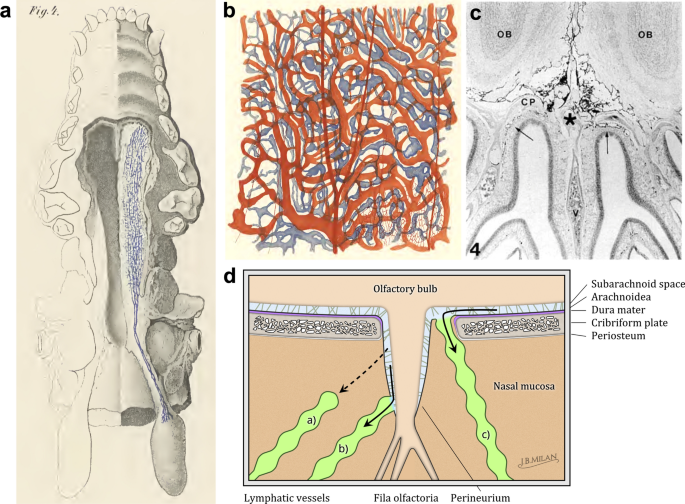
Anatomy and physiology of cerebrospinal fluid - ScienceDirect Vital stains injected into CSF spaces are subsequently found in the nasal submucosa and cervical lymph nodes , .This absorption pathway participates in the elimination of proteins and red blood cells from the CSF in cats and rabbits , and could be involved in the immune defense mechanisms of the brain .The lymphatic circulation would be a preferential pathway of absorption of cerebral ...
Cerebral circulation & csf formation - SlideShare CSF ( Cerebrospinal fluid physiology) circulation upendra bhardwaj. Y2 s1 csf vajira54. Csf formation, absorption and circulation Dr Sara Sadiq. Csf circulation and low csf pressure headaches ... (midline view) showing the anatomical structures involved in the production and flow of cerebrospinal fluid through the ventricular system, brain and ...
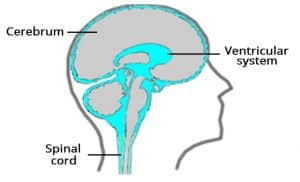
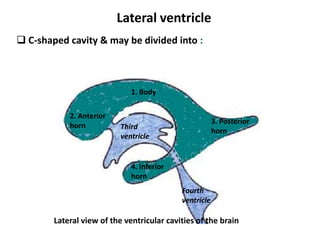
Cerebrospinal fluid flow: Anatomy and functions | Kenhub Cerebrospinal fluid circulates through a system of cavities found within the brain and spinal cord; ventricles, subarachnoid space of the brain and spinal cord and the central canal of the spinal cord. Most CSF is secreted by the specialized tissue called the choroid plexus, which is located within the lateral, third and fourth ventricles.
Cerebrospinal Fluid Dynamics Relevant to Hydrocephalus There are four ventricles in all: two lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle. The ventricles are connected by narrow passageways. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) flows through the four ventricles and then flows between the meninges in an area called the subarachnoid space.
A&P Lab Exercises 17&19 Flashcards | Quizlet Saggital view of the human brain stem and diencephalon 1) cerebral hemisphere (cat) 2) corpus callosum (cone) 3) septum pellucidum (saw) 4) fornix (fighting) 5) intermediate mass (in) 6) hypothalamus (high) 7) optic chiasma (off) 8) mammillary bodies (mansion) 9) pituitary gland (properties) 10) choroid plexus 11) thalamus 12) pineal gland
Solved 10. Label the structures involved with circulation of - Chegg Label the structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid on the accompanying diagram Add arrows to the figure above to indicate the flow of cerebrospinal fluid from its formation in the lateral ventricles to the site of its exit from the fourth ventricle. Then fill in the blanks in the following paragraph.
The function and structure of the cerebrospinal fluid outflow system ... The functional anatomy of the structures responsible for the return of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to the general circulation is based on somewhat conflicting evidence as to their location, anatomical features, and functional capabilities.
A new look at cerebrospinal fluid circulation | Fluids and Barriers of ... According to the traditional understanding of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) physiology, the majority of CSF is produced by the choroid plexus, circulates through the ventricles, the cisterns, and the subarachnoid space to be absorbed into the blood by the arachnoid villi. This review surveys key developments leading to the traditional concept.
Cerebrospinal fluid dynamics and intracranial pressure elevation in ... The fine balance between the secretion, composition, volume and turnover of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is strictly regulated. However, during certain neurological diseases, this balance can be disrupted. A significant disruption to the normal CSF circulation can be life threatening, leading to increased intracranial pressure (ICP), and is implicated in hydrocephalus, idiopathic intracranial ...
Solved > 14.Label the structures involved with circulation of ... 14.Label the structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid on the accompanying diagram. Add arrows to the figure above to indicate the flow of cerebrospinal fluid from its formation in the lateral ventricles to the site of its exit from the fourth ventricle. Then fill in the blanks in the following paragraph. Solution 5 (1 Ratings )
Circulation of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Flashcards | Quizlet Central canal of spinal cord 2. To the subarachnoid space via : two lateral apertures (holes or gaps) & one median aperture 3. Through extensions called arachnoid villi that delivers the CSF back into the superior sagittal sinus Arachnoid villi form large clusters in adults, called arachnoid granulations Circulation of CSF Circulation of CSF 2
The function and structure of the cerebrospinal fluid outflow system The functional anatomy of the structures responsible for the return of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to the general circulation is based on somewhat conflicting evidence as to their location, anatomical features, and functional capabilities.










:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/granulationes-arachnoideae/7I2XnLkmYhYFW8IUFoP2w_Arachnoid_granulation.png)










Post a Comment for "40 structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid"