39 biology plant cell
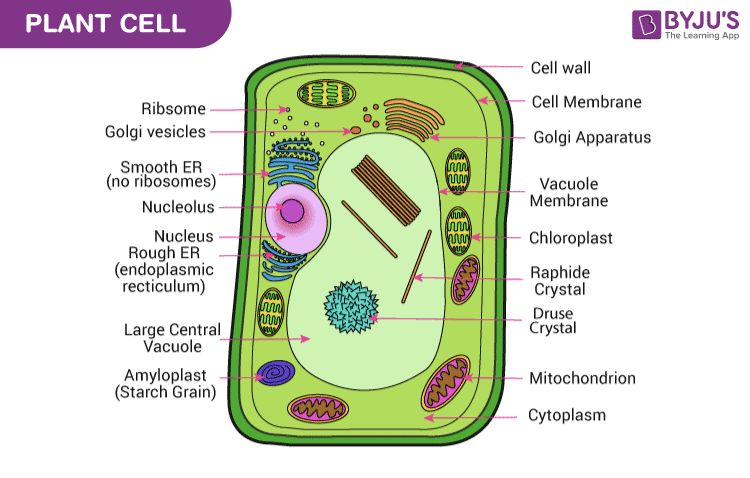
Plant Cells | Basic Biology Structure of plant cells Nucleus. The nucleus is where DNA is housed in the cells of plants. A nucleus consists of the cell's DNA and a nucleolus... Plasma membrane. All plant cells have a plasma membrane. This is a membrane that surrounds the inner contents of the... Cell wall. In plant cells the ... Types of Plant Cell- Definition, Structure ... - The Biology Notes Plant cells are multicellular eukaryotic cells that make up a plant (a group of eukaryotes belonging to the Plantae kingdom, with the ability to synthesis their own food using water, Sunlight, and CO2). Being eukaryotic cells, they have a defined nucleus with specialized structural organelles that enable them to function in an orderly manner.
Plant Cells: Crash Course Biology #6 - YouTube Hank describes why plants are so freaking amazing - discussing their evolution, and how their cells are both similar to & different from animal cells.This vi...
Biology plant cell
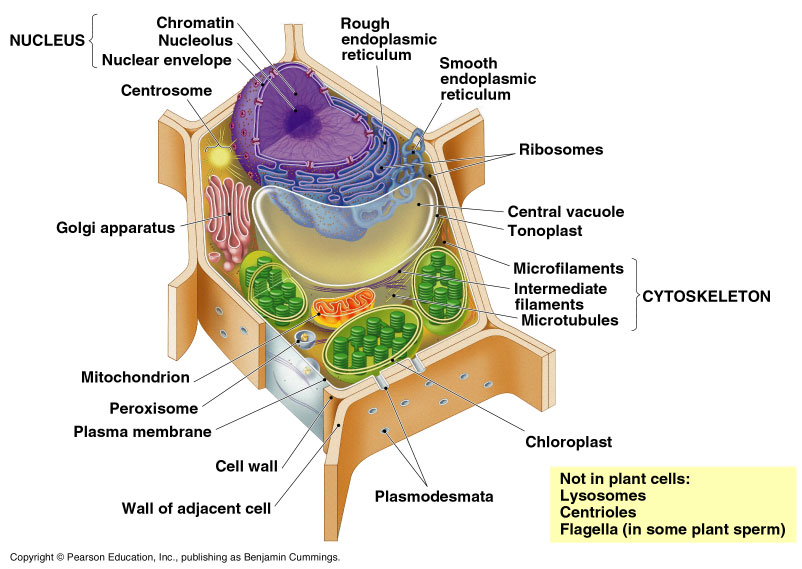
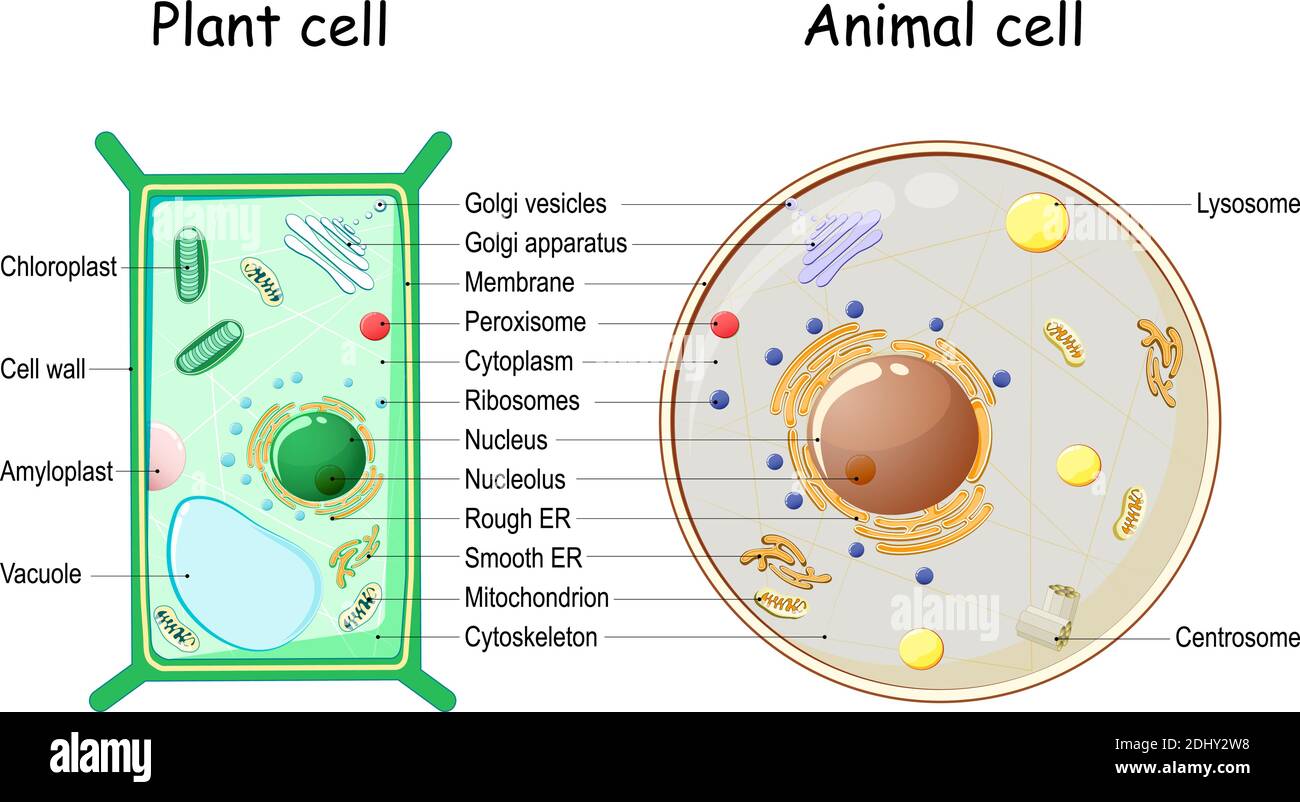
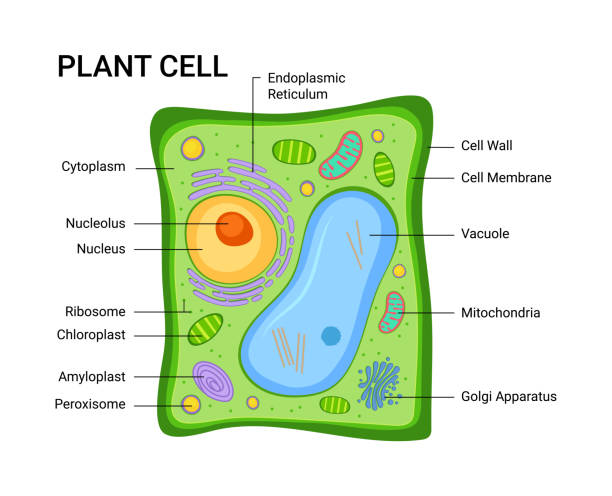
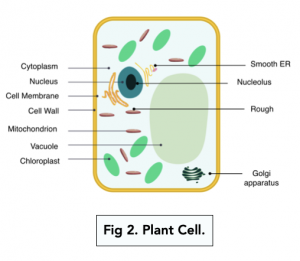
Plant Cells | Biology for Majors II - Lumen Learning Plant Cells Plant cells resemble other eukaryotic cells in many ways. For example, they are enclosed by a plasma membrane and have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. A typical plant cell is represented by the diagram in Figure 2. Figure 2. Plant cells have all the same structures as animal cells, plus some additional structures. Plant Cell - Definition, Diagram, Parts, Function, Structure & Types Let's know about the functions of these cells in detail: Parenchyma Cells: These are the cells that are majorly present in plants. They help in the metabolism and food... Sclerenchyma Cells: Sclerenchyma cells give the maximum support to the plant because of their hardness. These cells are... ... PDF Plant cell - Cornell University plant cells is the rigid cell wall, a feature that is typically absent in animal cells. However, any classification system is imperfect and some plant cells, such as those of the green alga Dunaliella, lack a rigid cell wall, whereas some animal cells, such as those in the tunica tes, have a rigid cellulosic cell wall. The range of
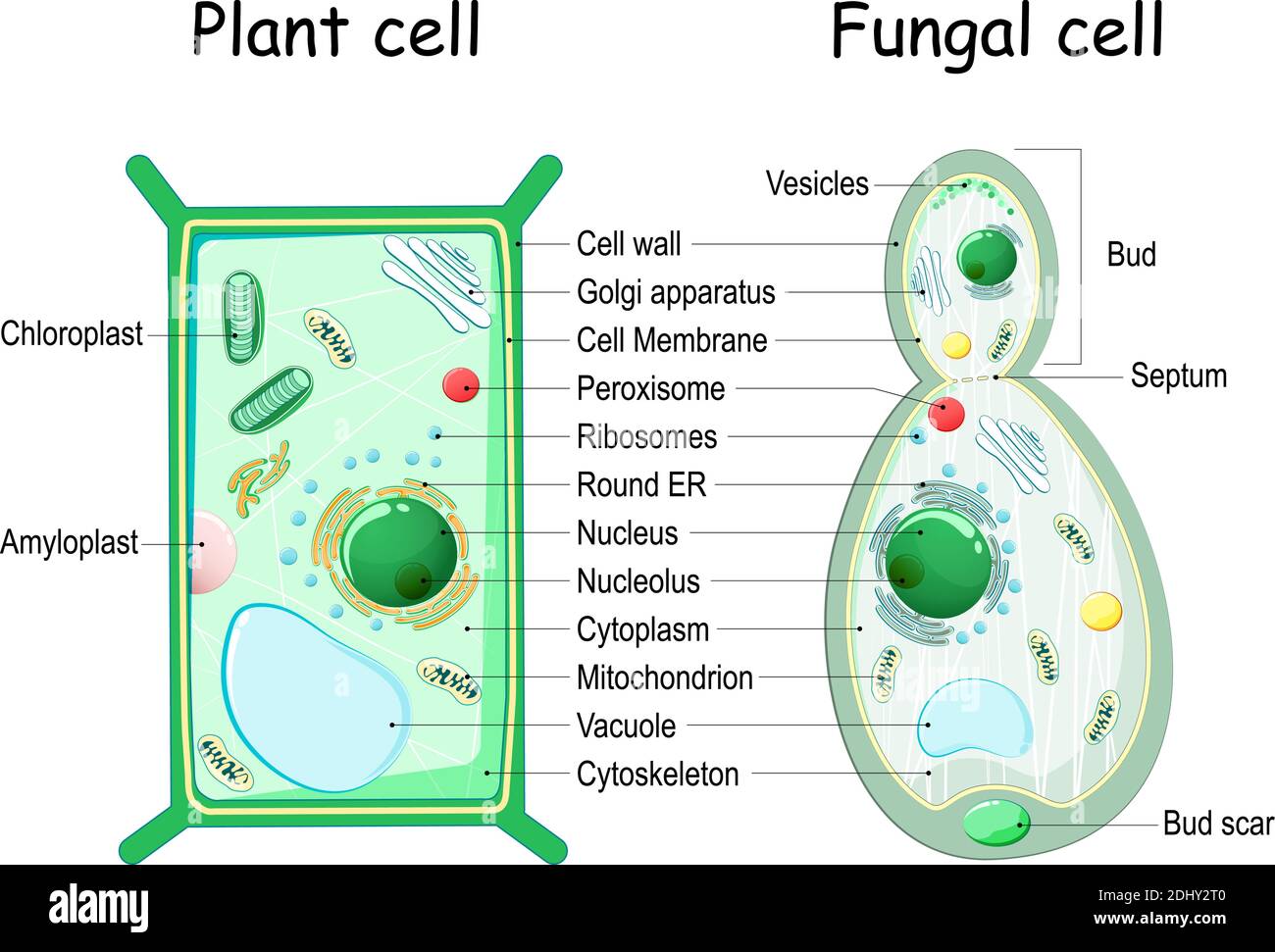
Biology plant cell. The Plant Cell - Wellesley College The Plant Cell Identify an organelle and then click on it to test your knowledge. Back to the Wellesley College Home Page. Back to the Biological Sciences Home Page. Created by Becky Schaefer and Marcy Thomas mthomas@wellesley.edu; Dept. of Biological Sciences; Created August 15, 1997; Plant cell biology - Latest research and news | Nature The Plant Cell | Oxford Academic An editorial innovation of The Plant Cell, one of the most trusted names in plant biology. Latest tools: Three-way interactions between plants, microbes, and arthropods Computational microscopy Browse all Voices for equity, diversity, and inclusion in STEM Plant cell - Wikipedia Plant cells have cell walls, constructed outside the cell membrane and composed of cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectin. Their composition contrasts with the cell walls of fungi, which are made of chitin, of bacteria, which are made of peptidoglycan and of archaea, which are made of pseudopeptidoglycan.
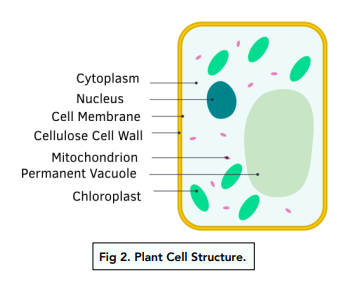
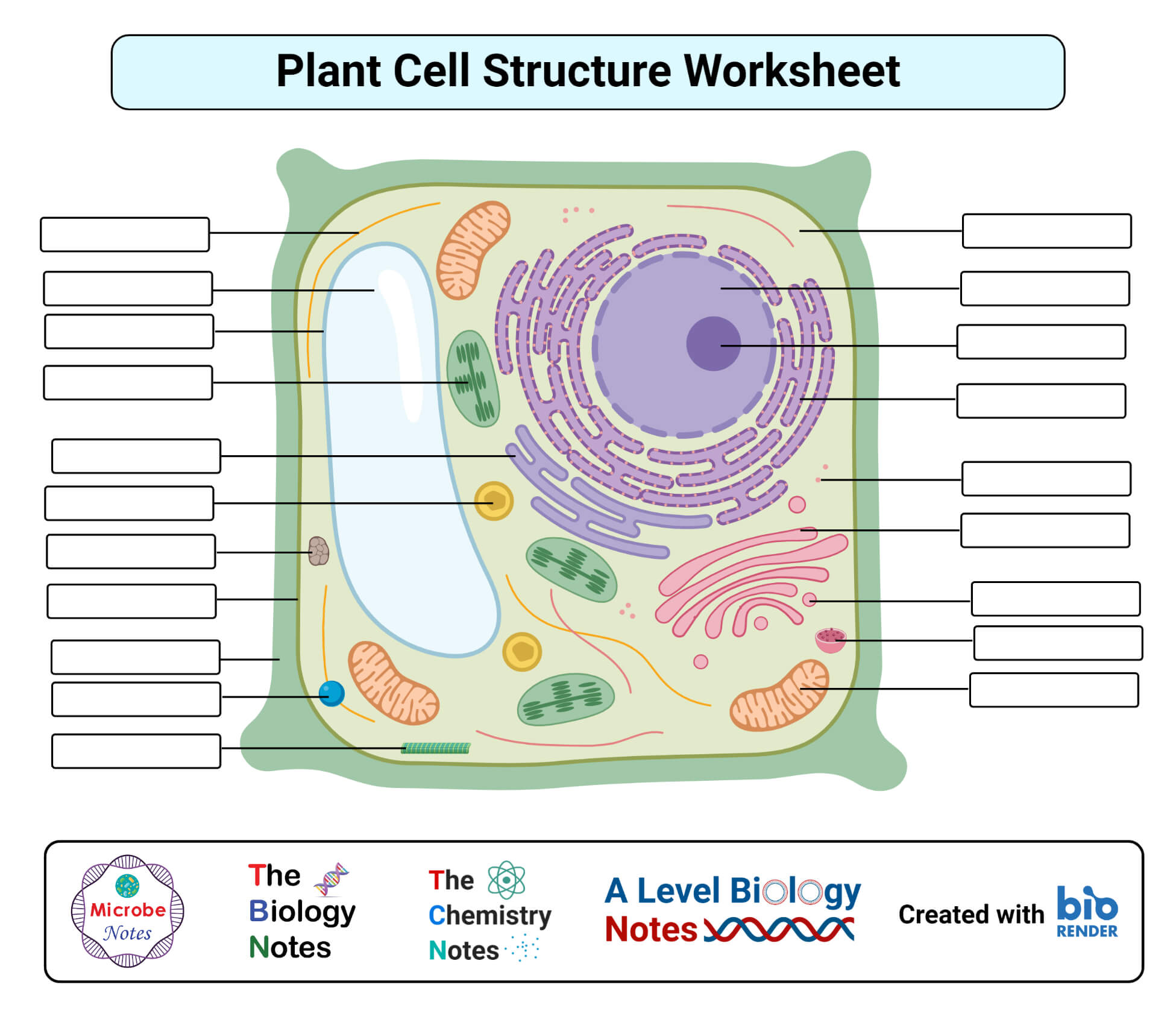
Plant Cell Organelles - Biology Wise A typical plant cell is made up of cytoplasm and organelles. In fact, all the organelles (except nucleus) and subcellular structures are present in the cytoplasm, which is enclosed by protective layers (the cell wall and cell membrane). Scientific studies have been done regarding the cell organelles and their functions. Plant Cells | Biology II - Lumen Learning Plant Cells Plant cells resemble other eukaryotic cells in many ways. For example, they are enclosed by aplasma membrane and have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. A typical plant cell is represented by the diagram in Figure 2. Figure 2. Plant cells have all the same structures as animal cells, plus some additional structures. Plant hairy roots for the production of extracellular vesicles with ... Plant extracellular vesicles (EVs) concentrate and deliver different types of bioactive molecules in human cells and are excellent candidates for a next-generation drug delivery system. However ... Plant cells (video) | Crash Course: Biology | Khan Academy Anyway, on a cellular level, plant and animal cells are actually pretty similar. They're called eukaryotic cells, which means they have a good kernel and that kernel is the nucleus. Not, new-cue-lus! And, the nucleus can be found in all sorts of cells. Animal cells, plant cells, algae cells, you know, basically all the popular kids.
Plant Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram Functions of the plant cell (plasma) membrane. In-plant cells the cell membrane separated the cytoplasm from the cell wall. It has a selective permeability hence it regulates the contents that move in and out of the cell. It also protects the cell from external damage and provides support and stability to the cell. Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells - ThoughtCo Plant cells are more similar in size and are typically rectangular or cube shaped. Energy Storage Animals cells store energy in the form of the complex carbohydrate glycogen. Plant cells store energy as starch. Proteins Of the 20 amino acids needed to produce proteins, only 10 can be produced naturally in animal cells. Plant Cell Parts & Functions | What is a Plant Cell? - Study.com Plants are eukaryotic organisms, meaning that their cell nucleus has a membrane around them. This nuclear wall or envelope is selectively permeable, meaning only certain things are allowed through... Plant Cell Definition, Function, Facts And Structure | Biology Topics Cell Wall. As the name suggests, the cell wall is the outer covering of the plant cell. The primary function of the cell wall is to protect the inner components of the plant cell. But, this is not its only function. This component is also giving the plant cell its shape. In the plant cell, the constituents of the cell wall are mainly: Cellulose.
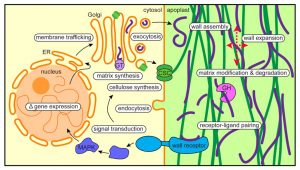
plant cell | Definition, Characteristics, & Facts | Britannica Plant cells, like animal cells, are eukaryotic, meaning they have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. The following is a brief survey of some of the major characteristics of plant cells. For a more in-depth discussion of cells, see cell. Unlike animal cells, plant cells have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane. Although often perceived as an inactive product serving mainly mechanical and structural purposes, the cell wall actually has a multitude of functions upon which plant life ...
Plant Cell Facts for Kids (Explained!) - Education site Fun Plant Cell Facts. Plant cells are unique - Plant cells are the only known things on earth that can produce their own food by themselves. Animals and plants are interdependent - The process of photosynthesis leaves oxygen that plants give off into the atmosphere. Animals and most of earth's life depend on that oxygen to live.
Plant Cell Biology | ScienceDirect Plant Cell Biology, Second Edition: From Astronomy to Zoology connects the fundamentals of plant anatomy, plant physiology, plant growth and development, plant taxonomy, plant biochemistry, plant molecular biology, and plant cell biology. It covers all aspects of plant cell biology without emphasizing any one plant, organelle, molecule, or technique. Although most examples are biased towards plants, basic similarities between all living eukaryotic cells (animal and plant) are recognized and ...
Plant cells - Cell structure - AQA - BBC Bitesize A tiny organelle where protein synthesis occurs. Plant cells also have additional structures: ...
Plant Cell Wall- Definition, Structure, Functions, Diagram The cell wall is present in the plant cell and absent in the animal cell which distinguishes them from each other. The cell wall is formed by the protoplast. Any plant cell which is devoid of the cell wall is called the protoplast. The plant cell is mostly made up of the following components: Cellulose Hemicellulose Pectin Protein
Teaching Tools in Plant Biology | The Plant Cell | Oxford Academic Every cell in the plant body needs the raw material for its activities. Plant physiology is the study of how these materials are acquired, synthesized, transported, and coordinated. Collection Tools and techniques Discovery is intimately tied to advances in research tools and methods.
Plant Cell - Definition, Structure, Function, Diagram & Types - BYJUS Plant Cell Types Collenchyma Cells. They are hard or rigid cells, which play a primary role in providing support to the plants when there... Sclerenchyma Cells. These cells are more rigid compared to collenchyma cells and this is because of the presence of a... Parenchyma Cells. Parenchyma cells ...
Plant Cell Organelles: Functions & Structures | StudySmarter Organelles in plant and animal cells. Plants have all the typical features of eukaryotic cells: plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, ribosomes, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, and cytoskeleton (Figure 1). You can go over our Eukaryotic Cells article for a quick review of the table comparing animal and plant cells.
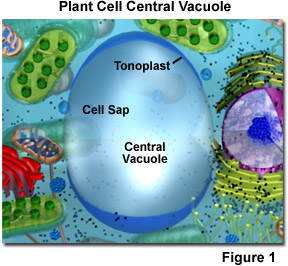
Plant Cell - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary Parts of a Plant Cell Chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are specialized organelles found only in plants and some types of algae. These organelles... Vacuoles. Plant cells are unique in that they have a large central vacuole. A vacuole is a small sphere of plasma... Cell Wall. The cell wall is a tough layer ...
PDF Plant cell - Cornell University plant cells is the rigid cell wall, a feature that is typically absent in animal cells. However, any classification system is imperfect and some plant cells, such as those of the green alga Dunaliella, lack a rigid cell wall, whereas some animal cells, such as those in the tunica tes, have a rigid cellulosic cell wall. The range of
Plant Cell - Definition, Diagram, Parts, Function, Structure & Types Let's know about the functions of these cells in detail: Parenchyma Cells: These are the cells that are majorly present in plants. They help in the metabolism and food... Sclerenchyma Cells: Sclerenchyma cells give the maximum support to the plant because of their hardness. These cells are... ...
Plant Cells | Biology for Majors II - Lumen Learning Plant Cells Plant cells resemble other eukaryotic cells in many ways. For example, they are enclosed by a plasma membrane and have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. A typical plant cell is represented by the diagram in Figure 2. Figure 2. Plant cells have all the same structures as animal cells, plus some additional structures.


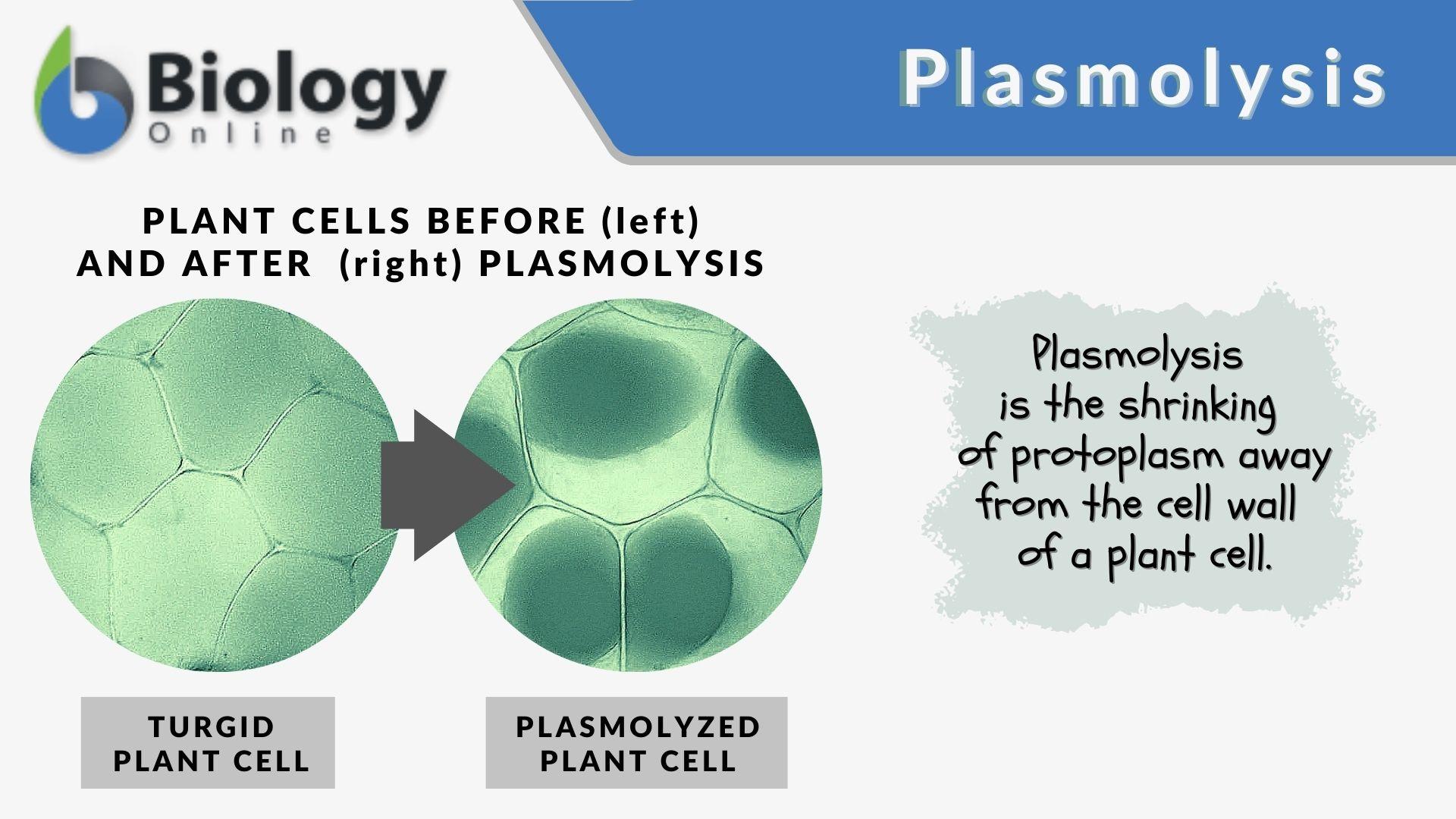






/plant-cell-elodea--isotonic-solution-shows-cells--chloroplasts-250x-at-35mm-139802547-5a956de86bf069003717851a.jpg)

















Post a Comment for "39 biology plant cell"